WHO tool for behavioural insights on COVID-19

A WHO tool for rapid, flexible and cost-effective monitoring of public knowledge, risk perceptions, behaviours and trust is now available to countries in the WHO European Region to make their COVID-19-related response relevant and actionable.
The outbreak is placing an overwhelming burden on health systems and authorities to respond with effective and appropriate interventions, policies and messages. One of the most critical elements of reducing virus transmission is public behaviour.
For crisis response measures to affect public behaviours, they need to be perceived as consistent, competent, fair, objective, empathetic or sincere. They also need to be easily understood and communicated through trusted people and accessible channels.
To succeed with this, it is critical to gain an understanding of issues such as:
- trust in health authorities, recommendations and information;
- risk perceptions;
- acceptance of recommended behaviours;
- knowledge;
- barriers/drivers to recommended behaviours;
- misperceptions; and
- stigma.
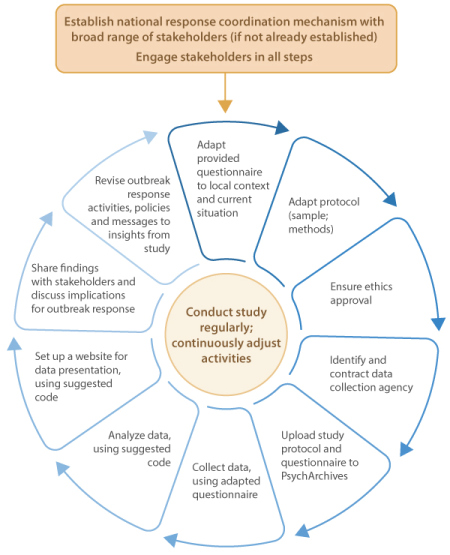
The newly established Insights Unit at WHO/Europe has developed a tool which:
- is evidence-based;
- can be rapidly applied;
- can be regularly applied;
- is simple and flexible to adjust to the changing situation; and
- is low cost and cost effective.
The tool is freely available to all. It has been developed in collaboration with the University of Erfurt, Germany, and the COSMO group, a consortium set up for such research.
By WHO Regional Office for Europe.
Read more
Recommendation for Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of New Infection
Clarification of local SARS prevention methods Temporary guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of new coronavirus infection (COVID-19), published by the Ministry of Health of Russia, contain information on the possibility of using an isotonic solution of sodium chloride as a method for preventing infection with coronavirus infection. In connection with the appeals of the media, the Ministry of Health of Russia clarifies.When acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI) occur, as a rule, the mucous membrane of the nose and throat is affected. This is manifested in the form of nasal congestion, perturbation and sore throat and is called rhinitis and pharyngitis, respectively. Coronavirus infection refers to ARVI, so approaches to prevention and symptomatic treatment are similar. A standard approach to the prevention and local treatment of rhinitis and pharyngitis is the use of an isotonic solution of sodium chloride (sometimes called "saline," often it is made on…
New tool for behavioural insights: critical to inform COVID response
New WHO/Europe tool for behavioural insights: critical to inform COVID-19 response WHO/Europe has released a new behavioural insights tool for national and local authorities developing and coordinating interventions, policies and messages for the COVID-19 response. Understanding public levels of trust, people’s perceptions of risk, and the barriers they may face in following recommended actions is critical to the effectiveness and success of pandemic response measures. Such insights into public behaviour form the basis of effective communication and can identify issues related to stigma or conspiracy myths, for example, as they emerge, thus ensuring that they are addressed quickly and effectively.“Rapid, simple and flexible to use, this behavioural…
Novavax received funds from the US government for a vaccine against COVID-19
Novavax gets $ 1.6 billion for COVID-19 vaccine Vaccine production may begin at the end of 2020. Novavax has received $1.6 billion from the U.S. government to conduct trials and produce a potential vaccine for the disease-causing coronavirus COVID-19. It is planned that by January next year, Novavax will be able to produce and deliver 100 million doses of the new vaccine to consumers.Novavax received the largest cash grant from America's Department of Health and Human Services as part of the U.S. government's Operation Super Light…